
WHAT IS ASSET MANAGEMENT
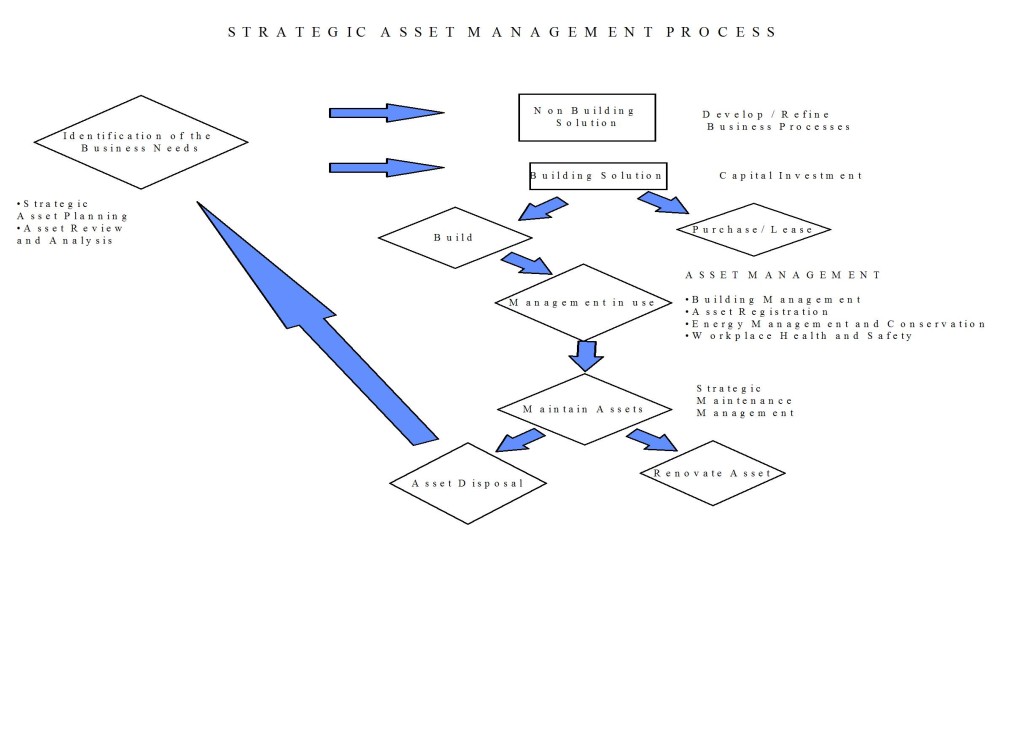
Strategic Asset Management, as it applies to built assets, entails the implementation of a “Whole of Life” process when considering the building, holding, renovating or disposal of assets. Such a process would ensure that all costs are considered prior to decision-making.
The direct risks associated with the condition of particular assets has been assessed and is included within the audit. This assessment is based on both the likely impact and the probability of an event occurring as a direct of the asset’s condition. The need to undertake works to bridge the gap between the existing and desired conditions has then been considered, taking into account the risks associated with letting the asset remain in its current condition.
Risks that have been considered include those that may adversely affect the business through disruptions or that expose the business to financial and/or legal implications. Risks include those that relate to:
- Workplace Health and Safety
- Security
- Functionality
- Financial Impact
- Legal Exposure
- Business Functionality
- Client Perceptions
STRATEGIC PLANNING

The aim of Strategic Asset Management is to gain the most from an asset over its whole lifecycle. This ensures that the owner gains whole of life value for money, and the asset user gains effective and efficient usage of the asset. The aim of strategic prioritization is to give the owner or facility manager recommendations as to which works should be completed based upon the specific and sometimes conflicting priorities of the owner/manager, legislation and good maintenance principles.
This prioritization process is based upon a number of criteria, including:
- How long the particular asset will be required to be in operation
- The future usage plans for the asset
- The owner/manager’s specific requirements for aesthetics
- The serviceability requirements of the asset
- The effect of not maintaining a particular asset
- The risks associated with not maintaining a particular asset
- The likely value adding of maintaining an asset
- The current condition of a particular asset
- Risk associated with the current condition
Through this process, risks are identified together with appropriate cost effective solution recommendations. Thus, maintenance activities may be undertaken in a planned manner to ensure appropriate risk control measures have been implemented while creating an environment that enhances the provision of Value for Money services. Maintenance funds may then be directed to areas of greatest need that meet the strategic directions set for the particular facility.

For clients with numerous buildings or complexes, this report can be tailored to prioritise works across those buildings or complexes. Also a general condition index may be given to each building or complex to give the owner / facilities manager specific information and an easy to use single number index to compare buildings or complexes.
ASSET REGISTER
Strategic Asset Management starts with the Asset Register. This is a complete listing of all properties owned by the organization and includes the property’s plant and equipment.
To effectively plan maintenance and upgrade of a facility, it is critical to have a complete and upto date Asset Register. Against each asset is a complete listing of inspection and maintenance tasks required under legislation and good maintenance practices. These include:
- Test and Tag
- Planned servicing
- Fire door testing
- Alarm system testing
- Planned re-painting programs
PROPERTY INVESTMENT DUE DILIGENCE
When a person or organization proposes the purchase of an existing business, a great deal of effort is devoted to conducting a “Due Diligence” investigation. This makes perfect business sense as the purchaser needs to know the accuracy of the information supplied to minimise the RISK.
However, very little consideration is given to the risks of purchasing a property. Most wise purchases will request a property inspection to identify the current condition. The major risks however are in the holding of the property.
QBM can minimise the risks of property investments by our Strategic Asset Maintenance Property Audit. This looks at the longer term, risks of holding a property for both the purchaser and the financing body.
PLANNING YOUR FACILITIES EXPENDITURE
A common comment by un-trained facility manager is “If its not broken, don’t fix it”.
Many an organization has faced severe financial hardship by adopting such a philosophy. This also contravenes many statutory requirements where regular testing and servicing is required.
Effective planning is critical not only to plan an organizations cash flow, but to protect the built assets. An organization should focus on maintenance as an essential activity to ensure that the organisation’s assets retain their quality and value to support the organizations service delivery. Be that selling a product or providing a service.
MAINTENANCE PLANS
Planning for maintenance should be undertaken on an annual basis with a planning horizon of at leat 3 years. The object being to have an identified program of maintenance activities and budgets each year.
BUDGETS
An organization should develop budgets and allocate funding for the maintenance of their buildings and equipment during the normal budgetary process. The level of these budgets will depend upon the complexity, age and condition of the assets. However, it is recommended that 1% of the assets value be considered as a minimum benchmark.
STATUTORY INSPECTIONS AND MAINTENANCE
Many items of plant and equipment require regular maintenance and servicing to abide by statutory regulations. It is critical that these are planned and budgeted to ensure complete compliance.
QBM’s systems are designed to accurately monitor and track these requirements to enhance compliance with legislation and to provide and effective level of Risk Management to the organization.
THE STRATEGIC AUDIT PROPERTY INSPECTION
The Strategic Property Audit Report will be prepared in accordance with the Australian Standard AS4349 – 1995 “Inspection of buildings”. However, much more information is included. This information considers the Risks associated with purchasing or holding this particular asset. The report is specifically designed to assist the owner/ facility manager raise Asset Management to the Strategic level.
Most inspections are visually based with the exception of electrical installations, where testing devices have been utilised and/or where special mention is made within the report. As detailed in the Standard, the following areas have been included for a condition assessment.
- The interior of the building
- The exterior of the building
- The roof space
- The underfloor space
- The roof exterior
- The site
- Common Areas
- Other buildings on site
- Building Equipment
The objective of this Strategic Condition Audit is to provide sufficient information of the condition of the asset to allow informed strategic asset planning and management decisions to be made.
The results of the audit, together with functionality, utilization and cost considerations may be used by the owner / facility manager to support decisions concerning the asset. These include:
- Maintenance Management
- Maintenance Strategic Planning
- Asset Review and Analysis
- Disposal Planning
- Life Cycle Planning
The benefits of such a process include:
- Establishment of the adequacy of current maintenance and capital funding
- Asset condition trends over time
- Effectively targeted and prioritized maintenance programs
- Identification of current and future maintenance liabilities
- Assessment of current maintenance strategies
To ensure funds are expended in the most effective and efficient manner, it is critical that the owner / facility manager develops Performance Standards for each particular asset. Performance standards are an integral part of the assessment process for this audit. These standards, as stipulated by the owner / facility manager have been included so that all recommendations given are prioritized based upon these standards.
These Performance Standards are based upon three broad principles, risk analysis, serviceability requirements and effects of not maintaining the asset. A rating standard based upon a 1 – 5 scale give an indication of the requirements set by the owner /facility manager. These ratings are listed below.





